- 작성일
- 2024.04.05
- 수정일
- 2024.04.05
- 작성자
- 나노
- 조회수
- 16
[PNU리서치]한동욱·홍석원·김윤학 교수팀 "나노 신소재 ‘맥신’ 근육 재생 효과 있다"
광메카트로닉스공학과 한동욱·홍석원 교수 연구팀과 융합의과학과 김윤학 교수팀이 미래 소재 혁신을 가져올 꿈의 물질로 각광 받고 있는 맥신(MXene) 나노입자의 근육 재생 효과를 검증하는 데 성공했다.
연구팀은 ‘체적 근육 손실(volumetric muscle loss, VML)’ 치료를 위한 맥신(MXene) 이식재 개발에 성공해, 맥신의 근분화(筋分化) 촉진 기전을 밝힌 연구 논문을 나노 및 마이크로 스케일의 연구와 응용 분야에서 세계적으로 인정받는 국제학술지 『나노-마이크로 레터스(Nano-Micro Letters)』 1월 4일자에 게재했다.
- 논문 제목: Highly Aligned Ternary Nanofiber Matrices Loaded with MXene Expedite Regeneration of Volumetric Muscle Loss(맥신을 포함한 정렬된 나노섬유 지지체를 활용한 체적 근육 손실 재생)
- 논문 링크: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40820-023-01293-1
‘체적 근육 손실(VML)’은 대규모 외상에 따른 골격근의 상당량(20% 이상) 손실을 의미한다. 이로 인한 근육 기능 상실과 같은 후유증이 있으며 의학계에서 조직공학 기반의 VML 치료 연구가 활발히 진행 중이다.
이번 연구에 활용된 ‘맥신(MXene)’은 이차원 나노입자로 구성된 물질로, 금속 카바이드나 탄화물을 에칭(etching, 표면을 부식시켜 제거·변형)해 얻어진다. 높은 전기전도성, 높은 열전도성, 우수한 기계적 강도 등의 물성을 갖고 있어 2011년 처음 발견된 이후 다양한 산업 분야에 활용돼 왔다. 최근에는 맥신의 여러 생물학적 특성이 알려지면서 생물·의학 분야에서 효능 연구가 이어지고 있다.
맥신의 생물학적 특성은 주로 독특한 구조적 특징과 관련 있다. 맥신 나노입자는 표면에 다양한 친수성 작용기를 갖고 있고, 페스츄리처럼 여러 개의 얇은 층으로 이뤄져 있어 여러 생체 분자 및 단백질의 흡착을 촉진한다. 이러한 특성을 통해, 맥신은 주변 세포의 부착을 유도하고 여러 신호전달 경로를 활성화시킨다. 또한, 특유의 광학적 특성과 낮은 독성, 화학적 개질(改質)이 용이한 특성 때문에 바이오센서, 의료용 이미징, 의료용 재료 등 다양한 분야에서 응용 가능성이 폭넓게 연구되고 있다.
부산대 연구팀은 맥신 나노입자와 콜라겐을 생분해성 의료용 고분자에 혼합해 정렬된 나노섬유 지지체를 제작했으며, 동물실험을 통해 이 지지체가 손상된 근육 조직의 빠른 재생을 촉진한다는 것을 확인했다.
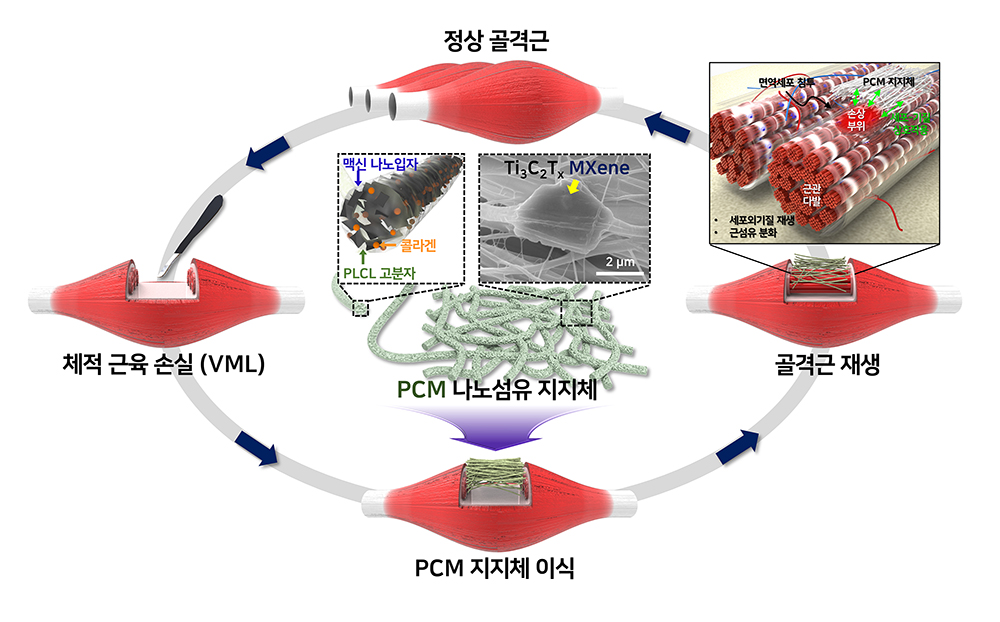
【맥신 나노섬유 지지체를 활용한 체적 근육 손실 재생 모식도】
부산대 연구팀은 맥신(MXene) 나노입자, 콜라겐, PLCL 의료용 고분자로 구성된 나노섬유 지지체(PCM 지지체)를 개발해,
마우스 체적 근육 손실(VML) 모델에 PCM 지지체를 이식한 후 평소보다 빠른 속도로 많은 양의 근육이 재생됨을 확인했다.
마우스 모델을 이용한 동물실험 결과, 비처치 대조군과 비교해 230% 빠른 근육 재생과 122% 많은 근섬유 재생이 확인됐다. 또한, 조직학적 분석을 통해 나노섬유 지지체 이식 일주일 후 대부분의 손상된 근육이 재생됐음이 관찰됐다.
이러한 결과는 맥신 나노입자에 의해 축적된 칼슘 이온이 근원세포의 생존, 증식, 근관 분화, 그리고 근단백질 합성을 유도하는 신호전달 경로(iNOS/SGK1-mediated mTOR-AKT pathway)를 촉진시켰기 때문임이 밝혀졌다. 결과적으로, 맥신 나노입자는 평소보다 빠른 속도로 많은 양의 근육을 재생시켜 체적 근육 손실을 빠르게 회복할 수 있었다.
한동욱 교수는 “근육 회복 과정에서 발현된 전체 유전자가 차세대 염기서열분석법(next-generation sequencing, NGS)을 통해 분석됐다”며 “이번 연구는 맥신 나노입자가 근분화를 촉진하는 분자생물학적 기전을 최초로 밝혔다는 데 의의가 있다”고 설명했다.
한 교수는 이어 “맥신 나노입자가 근육 재생에 대한 유망한 치료법으로 활용될 수 있다는 가능성을 보였으며, 추가 실험 및 공정 최적화를 통해 실제 임상에서도 활용될 수 있는 조직공학 기반 의료기기로 개발할 수 있을 것으로 기대한다”고 말했다.
이번 연구는 인지메카트로닉스공학과 강문성 박사과정생, 의과대학 의학연구원 유연이 박사(연수연구원), 인지메카트로닉스공학과 박로운 박사과정생이 공동 제1저자, 한동욱 교수, 홍석원 교수, 김윤학 교수가 공동 교신저자로 수행했다.
산업통상자원부 재원으로 수행된 한국산업기술평가원 바이오산업핵심기술개발 사업, 과학기술정보통신부 재원으로 수행된 한국연구재단 바이오·의료기술개발사업, 정부(과학기술정보통신부, 산업통상자원부, 보건복지부, 식품의약품안전처) 재원의 범부처전주기의료기기연구개발사업단 등의 지원을 받았다.
* 인물 사진: 왼쪽부터 홍석원 교수, 한동욱 교수, 김윤학 교수.
[Abstract]
Researchers at Pusan National University have achieved a groundbreaking milestone by confirming the muscle regeneration potential of MXene nanoparticles, a material anticipated to drive future innovations.
Pusan National University, led by President Jeong-In Cha, revealed on the 25th, that a collaborative research team, headed by prof. Dong-Wook Han and prof. Suck Won Hong (Dept. of Cogno-Mechatronics Engineering), in conjunction with prof. Yun Hak Kim (School of Medicine), has successfully developed MXene-including nanofibrous matrices for treating volumetric muscle loss (VML). This research was published in the 4th January in ‘Nano-Micro Letters’, a globally recognized journal focusing on multidisciplinary research in nano- and micro-scale materials.
MXene is two-dimensional nanoparticles obtained through etching metal carbides or nitrides. MXene's unique structural features hydrophilic functional groups and thin layered morphology, which result in specific optical properties, low toxicity, and easy chemical modification. These extraordinary characteristics endow them possibility to be applied in diverse biomedical fields such as biosensors, biomedical imaging, and medical devices.
Han et al. reported that the developed hybrid nanofiber matrices, combining collagen, poly(l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) (PLCL), and MXene, showed 230% faster muscle regeneration and 122% more regenerated muscle fibers compared to the untreated control group. The underlying biological mechanism was unveiled, triggered by the accumulation of calcium ions within MXene, activating the iNOS/SGK1-mediated mTOR-AKT pathway. This activation fosters the survival, proliferation, myogenic differentiation, and protein synthesis of myoblasts.
prof. Han emphasized the significance of the study, highlighting that it is pioneering attempt to unveil the biological mechanism by which MXene nanoparticles promote muscle differentiation. He expressed optimism about MXene's potential as a promising treatment for muscle regeneration, planning further experiments and optimization to develop MXene nanofibrous matrices into a tissue engineering-based medical device for clinical translation.
* Reference
- Authors (Pusan National University): Moon Sung Kang (Dept. of Cogno-Mechatronics Engineering, College of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology), Yeuni Yu (Medical Research Institute, School of Medicine), Rowoon Park (Dept. of Cogno-Mechatronics Engineering, College of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology), Suck Won Hong (Dept. of Cogno-Mechatronics Engineering, College of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology), Yun Hak Kim (Medical Research Institute, School of Medicine), Dong-Wook Han (Dept. of Cogno-Mechatronics Engineering, College of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology)
- Title of original paper: Highly Aligned Ternary Nanofiber Matrices Loaded with MXene Expedite Regeneration of Volumetric Muscle Loss
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40820-023-01293-1
- Journal: Nano-Micro Letters
- DOI: 10.1007/s40820-023-01293-1
- 첨부파일
- 첨부파일이(가) 없습니다.
